Business Environment Analysis: Why It Matters


Many variables determine the success or failure of a business, including the environment in which it operates. While we can’t control the ebb and flow of market changes, we can analyze the environment and make better-informed decisions.
This article will discuss business environment analysis, types of business environments, business atmosphere and the value it brings to businesses.
Let’s first define the business environment.
Business Environment in Nutshell

A business environment refers to the forces that influence the operations and growth of organizations. These forces could be internal, for example, HR policies and customers’ expectations, or external, for instance, government regulations and technological innovations.
So what is the best definition of the business environment? We believe that this concept should be described from different angles. Business environments can be characterized as follows:
- In interdependent environments, elements are linked so that if one element changes the others are affected.
- In dynamic environments, one or more elements are constantly changing, for example, consumer behaviors or technological development.
- In relative environments, the environmental elements differ depending on the location of the business.
- Uncertain environments are business environments that are hard to predict.
- In multi-faceted environments, environmental changes are either a threat or opportunity depending on the business. For example, the pandemic lockdowns boosted online businesses but set back restaurants.
Managers can only make strategic decisions when they understand their business environment and how it affects performance and profitability. So, it became evident that businesses must monitor their environment to make informed business decisions.
4 Types of Business Environments
Having defined and characterized a business environment, let’s look at the four types of business environments:
1. Internal Business Environment
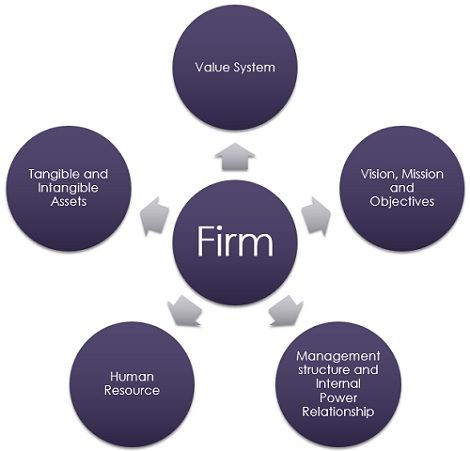
The internal business environment, directly controllable by an organization, significantly influences its growth and profitability. It encompasses factors like company culture, organizational structure, physical resources, and HR policies and processes. A positive work culture can greatly impact profitability, potentially leading to four times revenue growth.
According to Forbes, companies with strong cultures have four times revenue growth.
The organizational structure affects decision-making, with hierarchical structures centralizing decisions, while horizontal ones distribute decision-making among stakeholders. Essential physical resources, such as computers for digital operations, determine a company’s competitive edge.
Lastly, the HR department is crucial in shaping company culture and competitiveness through strategic recruitment and talent development, using tools like HR software to enhance these processes.
2. External Business Environment
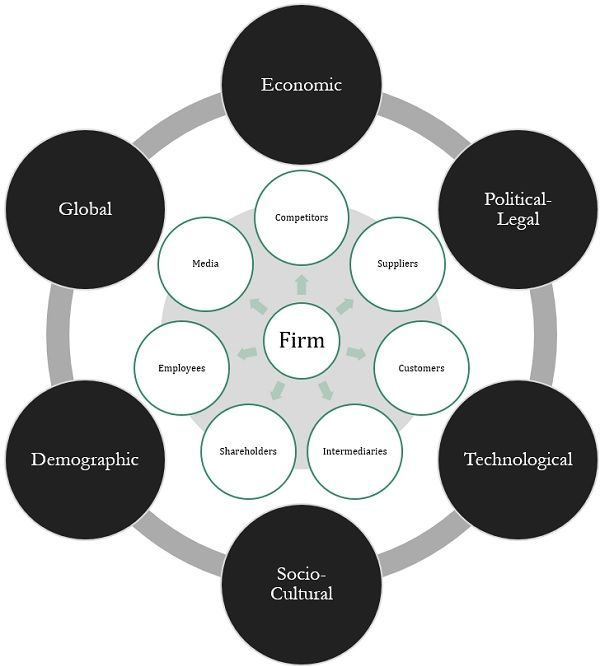
The external business environment is comprised of forces around the business that affect growth and profitability. Businesses can’t control them, and therefore can’t change them. For example, new import tariffs can affect the availability and price of a product.
The diagram illustrates how a business interacts with their external environments – it has direct interactions with the micro environment within the context of the macro environment.
Your company has an interdependent relationship with its external environment. It takes raw materials and returns products and services.
There are two groups of external environments: micro environment and macro environment.
3. Micro Business Environment
The micro environment impacts an organization’s daily operations and includes distributors, competitors, consumers, and the general public. Suppliers are vital for operational efficiency, as seen in e-commerce startups relying on web hosting services; their performance directly affects sales and customer satisfaction.
Competition, both local and international, necessitates offering superior customer value in price or quality to lead the market. The general public, encompassing media, citizens, and associations, can influence a business’s brand reputation significantly, impacting its response to PR crises.
4. Macro Business Environment
The macro-environment, affecting organizational decisions, comprises political, economic, social, and technological factors. Political climates influence decision-making, with stability and policies varying by country. Economic conditions, tied to political systems, affect customer purchasing power and include metrics like GDP and employment rates.
Failure to account for social determinants can lead to disastrous decisions and equal consequences, like when Nike faced backlash from the Muslim community over their Air Max shoe that resembled the Arabic word for God. Nike has since removed the offending logo from the shoe line.
Technological advancements offer opportunities but also challenge existing practices, necessitating careful evaluation of new technologies for competitive advantage. Understanding these macro factors is crucial for strategic planning, as they collectively form the business atmosphere that influences operational, growth, and decision-making processes in businesses.
For instance, if you can anticipate new legislation around customer data privacy, you can consult experts on how the law will affect your use of email marketing software. You can get ahead of your competitors by implementing appropriate changes, improving your brand reputation, and increasing customer loyalty.
The totality of all types is called business atmosphere and it’s the general mood, climate, or set of conditions that affect the way businesses operate, grow, and make decisions.
Business Environment Analysis: Defenition, Elements, Model
The business environment analysis process consists of the following steps:
- Identifying environmental determinants: Environmental determinants vary by industry; for example, legal determinant like health and safety are more salient in the medical field than social media management.
- Research: Use new reports or industry content materials to gather information. Government bodies are great sources of new industry material businesses can use. For instance, the Bureau of Economic Analysis comes up with reports on personal consumption expenditures. It also releases data like personal income and international transactions every year.
- Competitor analysis: Monitor what your competitors are doing and assess their level of threat. You can compile all your data in a report on a competitor’s digital presence made for a real company.
- Forecasting: Use data from your research and competitors to brainstorm scenarios on the impact of each environmental determinant. Organize your data in such a way you can properly visualize each scenario.
- Strategy development: Find solutions to mitigate potential threats and capitalize on opportunities. Specify, based on your collated data, the best steps to take to ensure business growth. This report by the Federated States of Micronesia is an excellent example of a strategic development plan that helps ensure the federated states achieve economic growth and self-reliance in 20 years.
Two Models for Business Environment Analysis
There are two models that target internal and external business environments. They are SWOT and PESTLE models respectively.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT Analysis is a strategic planning tool used to identify and understand the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats related to business competition or project planning. This framework helps organizations in assessing both internal and external factors affecting their operations.
- Strengths: Internal attributes and resources that support a successful outcome.
- Weaknesses: Internal attributes and resources that work against a successful outcome.
- Opportunities: External factors the organization can capitalize on or use to its advantage.
- Threats: External challenges the organization may face that could hinder its success.
SWOT Analysis is particularly useful for identifying the current position of a business or project and planning for future directions by maximizing strengths and opportunities while minimizing weaknesses and threats.
PESTLE Analysis
PESTLE Analysis is a comprehensive tool used to examine the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors affecting an industry or a business. This framework helps organizations in understanding the broader landscape in which they operate and in making strategic decisions.
- Political: Government policies, political stability, tax policies, trade restrictions, and labor laws.
- Economic: Economic growth, exchange rates, inflation rates, interest rates, and economic cycles.
- Social: Cultural trends, demographics, population analytics, and lifestyle changes.
- Technological: Technological advancements, innovation, automation, and research and development.
- Legal: Legislation affecting the business, regulatory bodies and processes, and changes in the law.
- Environmental: Environmental and ecological aspects, sustainability, and environmental regulations.
PESTLE Analysis is invaluable for organizations looking to venture into new markets or industries, planning long-term strategies, or understanding the external pressures they face. It provides a bird’s-eye view of the macro-environmental factors to consider for informed decision-making and strategic planning.
Practical Considerations: Commercial Environment
The commercial environment encompasses all the external and internal aspects that influence a company’s ability to trade and operate effectively. It is a broad term that covers various aspects of the business landscape, including market conditions, competition, regulatory frameworks, economic policies, technological advancements, and social trends.
Here are the key components of the commercial environment:
Market Conditions
- Demand and supply dynamics. The balance between what is available and what consumers want affects pricing, availability, and the viability of launching new products or services. This is the most well-known aspect of the commercial environment.
- Consumer trends and preferences. Changes in consumer behavior, preferences, and spending habits can influence product development, marketing strategies, and sales approaches. This is another well-known determinant of the commercial environment.
Competition
- Industry rivals. The number and strength of competitors within the market affect market share, pricing strategies, and the need for innovation.
- New entrants. The threat of new businesses entering the market impacts existing companies’ strategies for maintaining competitive advantage.
- Substitutes. Availability of alternative products or services can influence customer loyalty and pricing.
Economic Policies and Conditions
- Interest rates. Affect borrowing costs for businesses and consumers’ spending power.
- Inflation. Impacts cost of goods sold and pricing strategies.
- Exchange rates. Influences the cost of importing goods and the competitiveness of exports.
Technological Advancements
- Innovation. New technologies can disrupt existing markets, create new opportunities, change the whole commercial environment and require businesses to adapt quickly.
- Digitalization. The extent to which businesses and their customers adopt digital technologies affects operations, marketing, sales channels, and the overall commercial environment.
Regulatory Frameworks
- Laws and regulations. Compliance with local, national, and international laws, including tax codes, labor laws, environmental regulations, and trade policies. It’s very crucial aspect of the commercial environment.
- Intellectual property rights. Protection of patents, trademarks, and copyrights essential for innovation and branding.
Social and Cultural Trends
- Social values and ethics. Consumer expectations around corporate social responsibility, ethical sourcing, and sustainability can influence business practices.
- Demographic changes. Age, income distribution, and population growth trends affect market demand and labor markets.
Globalization and International Aspects
- Global trade agreements. Influence tariffs, access to markets, and competition.
- Political stability and economic conditions abroad. Impact global supply chains, market opportunities, and risk management.
Understanding the commercial environment requires continuous analysis as these determinants are dynamic and interrelated. Businesses that effectively navigate the commercial environment can identify opportunities for growth, mitigate risks, and build strategies that leverage their strengths in alignment with external trends and changes.
SumatoSoft is Your Reliable Technological Partner in the Ever-Changing World

Every project we undertake starts with nuanced business analysis. We have more than 150 successful projects in various industries like eCommerce, Elearning, Finance, Real Estate, Transport, Travel, and more. After more than 10 years of work, we have established a stable software development process for various time and budget limitations.
- Thanks to our strong commitment to deadlines and their needs, our client’s satisfaction rate is 98%
- We use the latest knowledge about business analysis in our work
- We have a deep expertise that allows us to develop the right solutions
- We are a member of The Council for Inclusive Capitalism
- We are recognized as top software developers by leading analyst agencies like Techreviewer, Clutch, and Goodfirms
- We are ready to offer your excellent results for a reasonable price
If you plan to develop a new software product, get in touch with us for a free consultation.
Key Takeaways
Business success is influenced by various factors beyond just the product or service offered, including the political climate, technology, and the cultural background of target consumers. Business must monitor their environment to make informed decisions.
Tools like SWOT and PESTLE are valuable for analyzing these environments, allowing businesses to identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, and to prepare for external challenges and opportunities by understanding the broader political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental landscape.
Let’s start
If you have any questions, email us info@sumatosoft.com